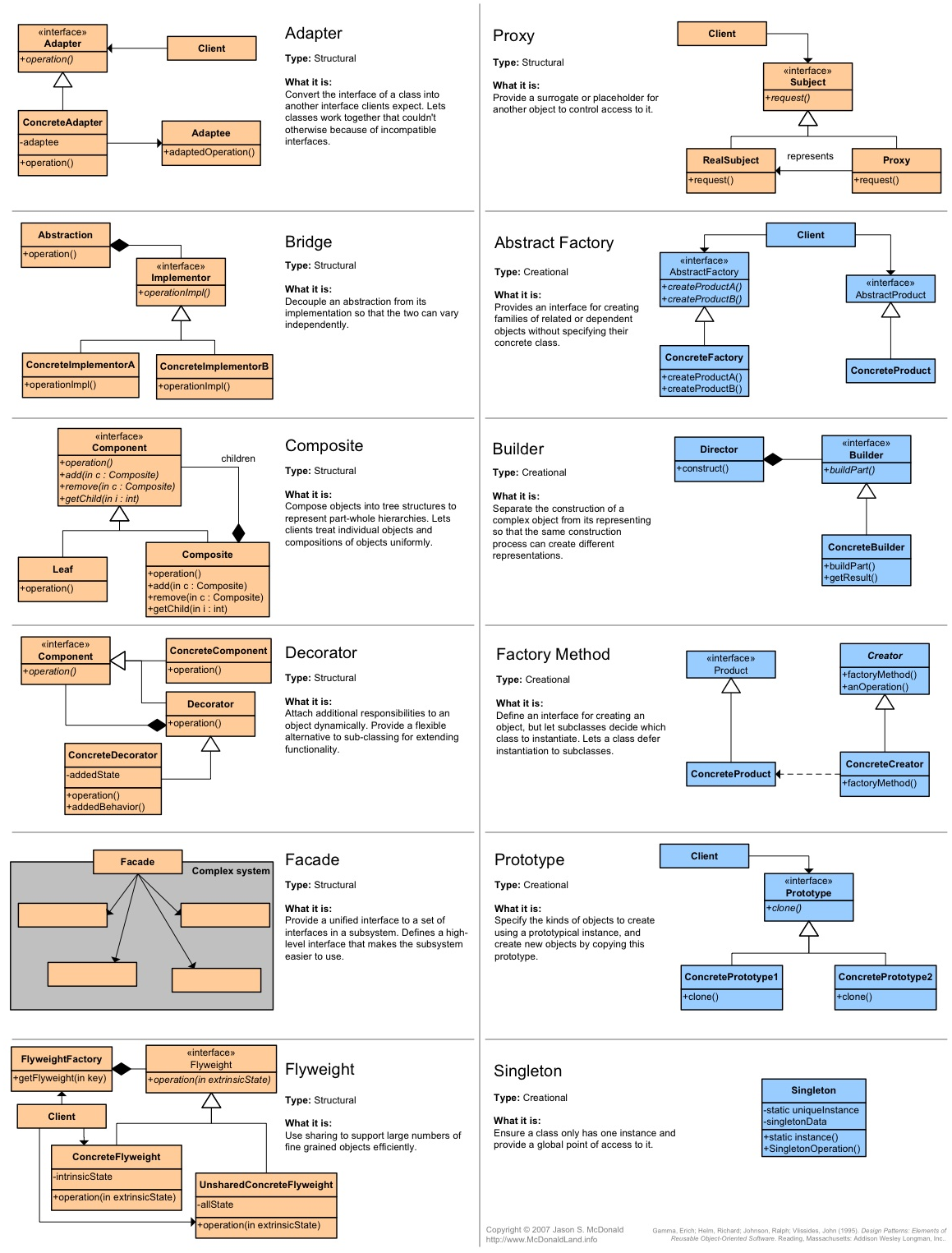
Overview of use-full design patterns:
Facade pattern
- A simple class is converted to a advance class
- The facade class serves as the class between the simple and the advance (Wrapper)
Adapter pattern:
- An advance class is adapted to a simple class
- The adapter class serves as the class between the advance and the simple (Wrapper)
Strategy pattern:
- Delegates functionality through a common interface, alternative to the decorator class
- The strategy class serve as the delegator to concrete strategy classes
- Example of strategy class is a string work, string-check or a string-sort class(look these up)
- Often utilizes polymorphism interfaces abstract and concrete classes and in heritage and composition.
- Main purpose is to add function interchangeability to classes. You can also add functions to classes at runtime as long as the interface of the function is the same
- Example:
assertIsEmailFormat(email).assertIsNotDisposableEmailService(email).isUnique(email)
Factory pattern:
- A builder class that builds classes upon requests
Example: makeSimpleButton(view).roundifyButton(view).addShadow(view).addTapCallBack(view, onTap)
Template pattern:
- A delegation class that utilizes an abstract class to control the order that functions in sub classes are run
- The class can utilize a hock function to disrupting the main algorithm flow. The order stays the same but functions can be omitted or behaviour changed
- Depends on inheritance
Memento pattern
- Saves and restores class states, can be used as undo redo and history functionality
- Becomes Truly useful when used with a dynamic flash_proxy class
Iteration pattern
Iterates over a list of items great way to delegate functionality to other classes
- Usually implements hasNext next and resets
- The iterator class restates inside a collection class that usually. Return an itereator or reverse-iterator class based on passed argument
Proxy pattern
- Is used to stand in for other objects such as files on remote servers
- Often a try catch function is involved . XML and constants as stand INS is a perfect example
Command pattern
- Encapsulated functions and invokes them in a sequence.
- Often used to add undo and redo. Functionality
Composite pattern
Hierarchical
Mediator pattern
- Works almost like a one level down singleton class
- A reference of the mediator class is passed down to sub classes an the sub classes then usually calls the mediators handle function with a state name as string. Then the handle function parses through a list of if else function and delegates functionality to the current state with a go function
- Add example: find on google:
swift mediator pattern example - With the mediator pattern, communication between objects is encapsulated within a mediator object. Objects no longer communicate directly with each other, but instead communicate through the mediator. This reduces the dependencies between communicating objects, thereby reducing coupling
Bridge pattern
- Two abstract classes that communicates then use concrete classes to customise the communication.
- Subclass with custom functionality. then call the common protocol
- Great example: https://medium.com/@iamcrypticcoder/bridge-pattern-in-swift-4-3472b56504b6
Builder pattern
- Creates a class and passes an iteratable array of function calls
- The builder pattern is veery useful when you need to configure the order the functions are called in the created class
Decorator pattern
- You decorate a class through composition rather than in-heritage.
- The decorator has the same interface as the class it decorates and usually also employ the use of a common abstract decorator class.
- One of the key benefits of using the decorator class is that you can change behaviour at runtime often without changing the class its decorating
- basically every decorator class holds a ref to the inserted instance. Think russian doll
Proxy pattern
- Similar to facade and adapter but have the same interface As the class it stands in for.
- Usually Delegates local info if remote info is not available.
Observer pattern
- Notification center etc
Visitor pattern:
- Visitor is a behavioural design pattern that allows adding new behaviors to existing class hierarchy without altering any existing code.
Flyweight pattern:
- to come
Design pattern Overview
Creational
- Abstract Factory
- Builder how a composite object gets created
- Factory Method subclass of object that is instantiated
- Prototype class of object that is instantiated
- Singleton the sole instance of a class
Structural
- Adapter interface to an object
- Bridge implementation of an object
- Composite structure and composition of an object
- Decorator responsibilities of an object without subclassing
- Facade interface to a subsystem
- Flyweight storage costs of objects
- Proxy how an object is accessed; its location
Behavioral
- Chain of Responsibility object that can fulfill a request
- Command when and how a request is fulfilled
- Interpreter grammar and interpretation of a language
- Iterator how an aggregate’s elements are accessed, traversed
- Mediator how and which objects interact with each other
- Memento what private information is stored outside an object, and when
- Observer number of objects that depend on another object; how the dependent objects stay up to date
- State states of an object
- Strategy an algorithm
- Template Method steps of an algorithm
- Visitor operations that can be applied to object(s) without changing their class(es)